Development of Environmentally Benign Bio-inspired Oxidation Catalysts
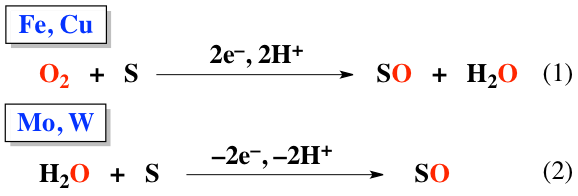
Our research objective is to evaluate the chemical functions of metalloenzymes, biocatalysts involving transition-metal ion(s) in their active-sites, and apply them to catalytic oxidation reactions. Our targets are iron- and copper-containing oxygenases and molybdenum- and tungsten-containing oxidoreductases. The iron- and copper-containing metalloenzymes, for example, bind molecular oxygen in the air to transport it to all over our body and reductively activate it by injecting electrons and protons (eq. 1) to accomplish a series of oxidation/oxygenation reactions of a variety of substrates. Such reactions are indispensable to prepare useful materials and to degrade harmful compounds in our body. On the other hand, metalloenzymes involving a molybdenum or a tungsten ion activates water molecule by abstracting electrons and protons (eq 2) to perform oxygen atom transfer to several organic and inorganic substances. These reactions (eq 1 & 2) afford very clean and environmentally benign processes since they employ very cheap molecular oxygen or water molecule as the oxygen source and produce no harmful byproducts. Thus, much recent attention has been focused on such ideal chemical processes.
生体触媒に学ぶ環境にやさしい酸化触媒の開発
我々は、活性中心に遷移金属を持つ酸化還元酵素の機能解明と、その触媒化学的応用をめざして研究を展開しています。
鉄(Fe)や銅(Cu)を含む金属酵素(金属タンパク質)は、空気中の酸素と結合して、それを体の隅々まで運んだり、結合した酸素を還元的に活性化して(式1)、様々な有機化化合物を酸化して有用な化合物に変換したり、分解して体の外へ排出したりする役割をになっています。一方、活性中心にモリブデン(Mo)やタングステン(W)を含む金属酵素は、水を酸化的に活性化して、色々な有機および無機基質への酸素原子移動反応を行っています(式2)。これらの反応は、地球上に無尽蔵に存在する分子状酸素や水を酸素源としており、有害な副生成物を出さないため、クリーンで環境に優しいものとして注目を集めています。我々はこのような金属酵素に含まれる反応活性種の構造、物理化学的特性(分光学的特性、磁気的特性、酸化還元電位)、および反応性について解明し、それぞれの相関関係を深く理解することで、金属酵素のストラテジー(戦略)を応用した新しい分子触媒が開発できると考えています。
In our laboratory, we are trying to evaluate the structures, physicochemical properties (spectroscopic, redox, and magnetic features), and reactivity of the active-oxygen species generated on the active-site transition-metal ion(s) and apply those strategies (eq 1 & 2) to develop efficient oxidation/oxygenation catalysts for practical applications. To accomplish these objectives, we employ several experimental techniques such as those of synthetic organic chemistry for the design and synthesis of new bio-inspired ligands, coordination chemistry for the synthesis of active-site model complexes, several spectroscopic techniques (UV-vis, IR, resonance Raman, fluorescence, X-ray crystallographic analysis, NMR, ESR, etc.) for structural and physicochemical evaluations, and electrochemistry and kinetics for mechanistic investigations. Furthermore, we are dealing with biochemistry of real proteins (enzymes), where not only mechanistic studies of the enzymes but also creation of novel artificial metalloenzymes are conducted by using advanced molecular biology techniques.
このような目的を達成するために、我々の研究室では、有機合成化学的手法を駆使した新しい配位子のデザインと合成、錯体合成化学的手法を用いた錯体の合成、各種分光学的手段(紫外可視、赤外、共鳴ラマン、蛍光、X線結晶解析、NMR、ESRなど)を利用した構造や物理化学的特性の評価、および電気化学や速度論的検討による反応機構の解明などを行っています。また、モデル錯体を用いた研究に止まらず、実際の酵素やタンパク質を用いた生化学的研究も行っており、ここでは最新の分子生物学の手法(遺伝子工学)を駆使したタンパク質(酵素)の設計と機能解明および機能創成などについて研究を展開しています。
↓ より詳細な研究内容紹介はこちら ↓